크레인 후크 검사 체크리스트: ASME, OSHA 및 GB 표준 설명
목차
이 글에서는 ASME, OSHA, GB 코드의 크레인 후크 검사 체크리스트와 표준을 각각 소개합니다. ASME는 미국기계학회(American Society Of Mechanical Engineers)의 약자입니다. OSHA는 미국 직업안전보건청(Occupational Safety and Health Administration)의 약자입니다. OSHA의 사명은 미국 근로자들이 불법적인 보복으로부터 안전하고 건강한 근무 환경을 보장하는 것입니다. GB 표준은 중화인민공화국 국가표준입니다.
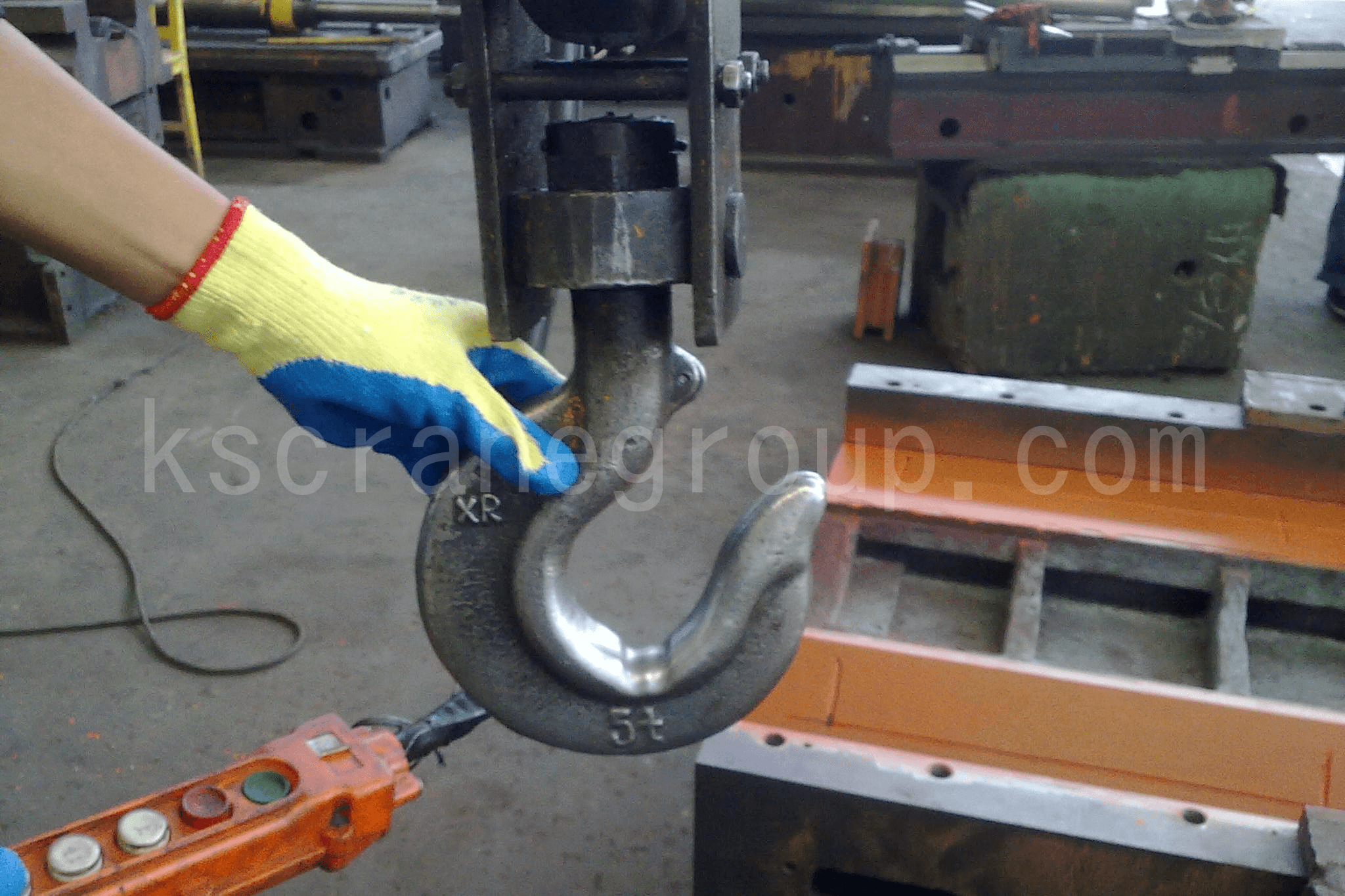

ASME B30.10 후크 검사
그만큼 ASME B30.10 표준 모든 호이스트, 크레인 및 조작 장치의 후크 검사를 담당합니다.
모든 검사는 지정된 담당자가 수행해야 합니다. 발견된 결함은 검사를 거쳐 자격을 갖춘 담당자가 위험 요소 여부를 판단해야 합니다.
정기적으로 사용되는 후크에 대한 검사 절차 및 기록 보관 요건은 후크가 사용되는 장비의 종류에 따라 결정됩니다. 특정 장비에 대한 표준에 후크에 대한 더 엄격한 요건이 명시된 경우, 해당 요건이 다음 요건보다 우선합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우, 최초 검사와 검사 수행 주기에 따른 두 가지 일반 분류가 적용됩니다. 본 문서에서는 최초 검사, 빈번 검사, 정기 검사로 분류하며, 검사 간격은 다음과 같이 정의됩니다.
초기 검사
사용하기 전에 모든 새 후크, 변경된 후크, 수정된 후크 또는 수리된 후크는 해당 규정을 준수하는지 확인하기 위해 검사해야 합니다. ASME B30.10 후크 표준입니다. 초기 검사에 대한 서면 기록은 필요하지 않습니다.
빈번한 검사
(a) 빈번한 검사에는 작동 중 사용되는 후크의 관찰과 함께 다음에 명시된 조건 또는 제거 기준을 식별하기 위한 시각적 검사가 포함됩니다. ASME B30.10 호이스트 후크 검사 지침.
(b) 빈번한 검사가 불가능한 반영구적이고 접근이 불가능한 위치의 경우 자격을 갖춘 사람이 정기 검사 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 빈도를 결정합니다. ASME B30.10 후크 검사 요구 사항.
(c) 검사 간격은 다음을 기준으로 해야 합니다.
- 후크 사용 빈도
- 서비스 조건의 심각성
- 화물 취급 활동의 특성
- 유사한 상황에서 사용되는 후크의 수명에 대한 경험
- 빈번한 검사 간격에 대한 지침(정상 서비스 - 월간, 중대 서비스 - 주 단위에서 월 단위, 심각 서비스 - 일 단위에서 주 단위)
(d) 제거 기준에 명시된 조건 또는 기타 위험을 초래할 수 있는 조건은 후크를 사용에서 제거해야 합니다. 후크는 자격을 갖춘 사람의 승인을 받기 전까지는 다시 사용할 수 없습니다.
(e) 빈번한 검사에 대한 서면 기록은 필요하지 않습니다.
정기 검사
(a) 후크에 대한 완전하고 철저한 검사를 수행해야 합니다. 후크를 완전히 검사하고 제거 기준에 따라 상태를 확인하기 위해 후크를 분해해야 할 수도 있습니다. ASME B30.10 후크 검사 요구 사항.
(b) 정기 검사는 자격을 갖춘 사람의 승인을 받지 않는 한 최소 12개월 간격으로 수행되어야 합니다. 정기 검사 간격은 다음을 기준으로 해야 합니다.
- 후크 사용 빈도
- 서비스 조건의 심각성
- 화물 취급 활동의 특성
- 유사한 상황에서 사용되는 후크의 수명에 대한 경험
- 정기 검사 간격에 대한 지침(정상 서비스 - 장비를 설치한 상태에서 매년; 중대 서비스 - 장비를 설치한 상태에서 반기마다, 외부 조건으로 인해 매월 또는 분기별로 자세한 검사를 허용하기 위해 분해해야 하는 경우 제외; 심각한 서비스 - 중대 서비스와 마찬가지로 분기별, 단 자세한 검사에서 비파괴 유형의 테스트가 필요할 수 있음)
(c) 자격을 갖춘 사람의 승인을 받기 전까지는 후크를 서비스에 다시 사용할 수 없습니다.
(d) 서면 기록이 필요합니다.
ASME B30.10 후크 제거 기준
다음과 같은 손상이 눈에 띄는 경우 후크를 서비스에서 제거해야 하며 반환해야 합니다.
자격을 갖춘 사람이 승인한 경우 서비스:
- 후크 제조업체 식별 또는 보조 제조업체 식별이 누락되었거나 읽을 수 없음
- 정격 부하 식별이 누락되었거나 읽을 수 없음
- 과도한 침식 또는 부식
- 균열, 흠집 또는 홈
- 마모 - 후크 또는 로드 핀의 원래 단면 치수의 10%(또는 제조업체 권장 사항)를 초과하는 모든 마모
- 변형 - 굽혀지지 않은 후크 평면에서 눈에 보이는 굽힘이나 꼬임
- 인후 개방 - 인후 개방이 5%로 증가하게 하는 왜곡은 1/4인치(6mm)를 초과하지 않거나 제조업체에서 권장하는 대로입니다.
- 잠금 불가능 - 잠금되지 않는 자체 잠금 후크
- 작동하지 않는 래치(제공된 경우) - 후크의 목을 닫지 못하는 손상된 래치 또는 제대로 작동하지 않는 래치
- 손상, 누락 또는 오작동하는 후크 부착물 및 고정 수단
- 나사산 마모, 손상 또는 부식
- 열 노출 또는 무단 용접의 증거
- 드릴링, 가공, 연삭 또는 기타 수정과 같은 무단 변경의 증거
OSHA 크레인 후크 검사
변형이나 균열이 있는 후크는 매일 육안 검사를 받아야 합니다. 또한, 검사일, 검사 담당자 서명, 검사 대상 후크의 일련번호 또는 기타 식별 정보가 포함된 인증 기록을 제출하여 월별 검사를 실시해야 합니다. 균열이 있거나, 정상적인 목구멍의 15%를 초과하는 구멍이 있거나, 굽히지 않은 후크 평면에서 10°를 초과하여 꼬인 후크의 경우, 구체적인 기준은 다음에서 확인할 수 있습니다. OSHA 1910.179.
OSHA 후크 제거 기준
- 가장 좁은 지점에서 측정한 인후 개구부는 원래 개구부보다 15% 이상 증가했습니다.
- 후크는 후크의 원래 평면에서 10° 이상 비틀렸습니다.
- 후크는 단면적의 10% 이상을 잃었습니다.
- 후크가 깨졌거나 다른 결함이 있습니다.
- 마모 또는 손상이 제조업체가 지정한 기준을 초과합니다.
크레인 후크 검사 기준의 GB 표준
GB/T 10051 단조 후크의 사용 중 검사 내용, 요구 사항 및 검사 간격을 지정합니다.
사용 전 검사:
- 후크의 표시는 제조업체의 적합성 인증서와 일치해야 합니다.
- 스트레이트 섕크 싱글 후크와 스트레이트 섕크 더블 후크의 표시는 각각 GB/T 10051.2-2010의 6.1절과 6.2절의 규정을 준수해야 합니다.
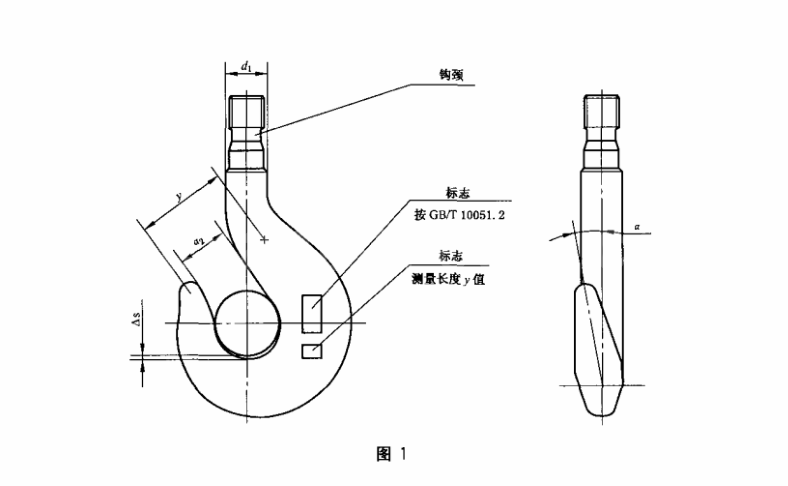
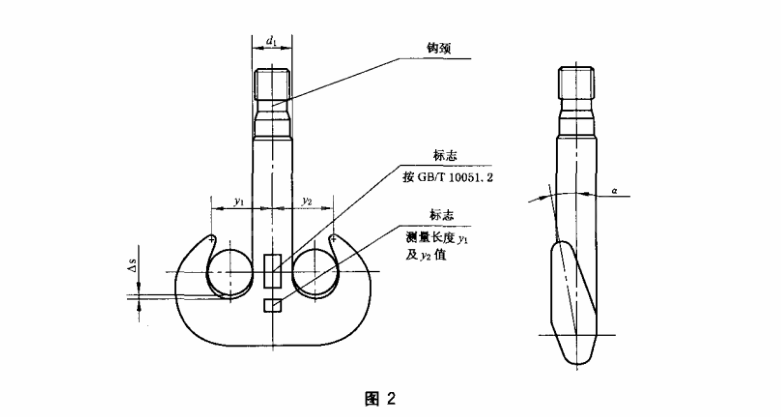
- 모델 번호가 006~5인 후크의 경우, 개구부 치수 a2를 다시 확인해야 합니다. 다른 후크 모델의 경우, 측정된 길이 y, y1, y2(그림 1 및 2 참조)를 확인해야 합니다. 단일 후크의 경우, 값은 GB/T 10051.4의 표 1 및 표 2 또는 GB/T 10051.5의 표 1을 준수해야 합니다. 이중 후크의 경우, 값은 GB/T 10051.6의 표 1 또는 GB/T 10051.7의 표 1을 준수해야 합니다.
사용 검사:
표면 균열
후크 표면에 균열이 있는지 검사하세요. 균열이 발견되면 후크를 폐기해야 합니다.
흉한 모습
- 모델 번호 006~5의 후크는 개구부 치수 a2를 검사해야 합니다. 다른 후크 모델의 경우, 측정된 길이 y, y1, y2(그림 1 및 2 참조)를 다시 확인해야 합니다. 측정값이 사용 전 치수의 10%를 초과하면 후크를 폐기해야 합니다.
- 후크의 비틀림 변형 여부를 검사하십시오. 후크 본체의 비틀림 각도 aa(그림 1 및 2 참조)가 10°를 초과하면 후크를 폐기해야 합니다.
- 후크의 샤프트는 어떠한 플라스틱 변형도 있어서는 안 됩니다. 변형이 있는 경우에는 폐기해야 합니다.
입다
후크의 마모 Δs(그림 1 및 2 참조)는 기본 치수의 5%를 초과해서는 안 됩니다(단일 후크의 경우 GB/T 10051.4-2010의 표 1, h2열 참조, 이중 후크의 경우 GB/T 10051.6-2010의 표 1, h열 참조). 마모가 이 한도를 초과하면 후크를 폐기해야 합니다.
부식
- 후크 섕크 직경 d1의 부식(그림 1 및 2 참조)은 기본 치수의 5%를 초과해서는 안 됩니다(단일 후크의 경우 GB/T 10051.4, 이중 후크의 경우 GB/T 10051.6 참조). 초과하는 경우 후크를 폐기해야 합니다.
- 후크의 실은 부식되어서는 안 됩니다.
후크의 결함은 용접으로 수리해서는 안 됩니다.
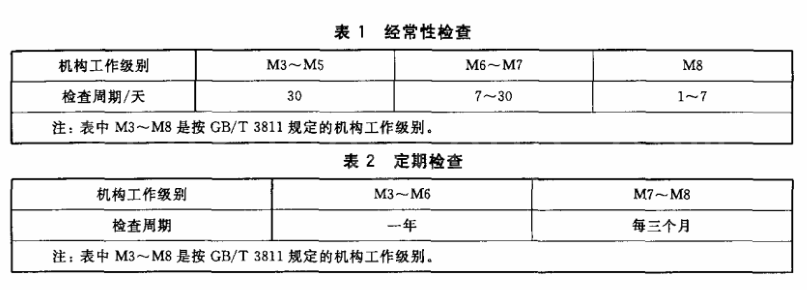
검사 간격 및 검사원:
- 빈도와 정기 검사 간격은 표 1과 표 2에 명시되어 있습니다.
- 운영자나 위임받은 다른 인력이 자주 검사를 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 정기 검사는 전담 검사 인력이 수행해야 합니다. 검사관은 본 조 3.2항의 요건에 따라 점검을 수행해야 합니다.
- 정기적인 검사는 문서화하고 보관해야 합니다.
- 특수한 사용 조건에 대해서는 별도의 규정이 제정될 수 있습니다.
우리가하는 일이 마음에 드십니까?공유

































































.png?w=200&h=134)



















