- EQUIPMENT
- special cranes
-
Industry Crane
-

Industry Crane
-

Tundish Cranes
-

Slab Cranes
-

Scrap Cranes
-

Billet Cranes
-

Coil,Bar and Plate Handling Cranes
-

Cement And Precast Crane
-

Power Station Crane
-

Ladle Cranes
-

Paper Industry Cranes
-

Waste to Energy Cranes and Biomass Cranes
-

Tailored Overhead Cranes for Aerospace: High Precision, Efficience, Safety and Reliability
-
-
Hoist & Winch Trolley
-

Casting Electric Wire Rope Hoist
-

European Model Electric Hoist
-

Explosion-proof Electric Hoist
-

Low-headroom Electric Hoist
-

Electric Chain Hoist
-

2 Types Explosion-Proof Electric Chain Hoists for Hazardous Zones: Gas & Dust Protection
-

2 Types Explosion-Proof Electric Wire Rope Hoists for Industrial Safety: Reliable Gas & Dust-Proof Solutions
-

Manual Hoists for Precision Lifting: Explore 3 Proven Types for Power-Free Operation
-
-
CRANE Spreader
-
Crane Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Turning and Side Hung
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Thick Plate
-

Specialized Electromagnet for Lifting Steel Plates
-

Lifting Electromagnets for Lifting Steel Plates
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Heavy Rail and Profiled Steel
-

Lifting Electromagnet for High Speed Wier(Coiled Bar)
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Rebar and Steel Pipe
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Bundled Rebar and Profiled Steel
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Billet, Girder Billet and Slab
-

Lifting Electromagnet for Steel Scraps
-
- Crane Spreader
- Crane Lifting Tongs and Clamps
-
Crane Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets
- CRANE PARTS
- Transfer Cart

Understanding Rail Standards: A Comprehensive Guide
20 Sep, 2023

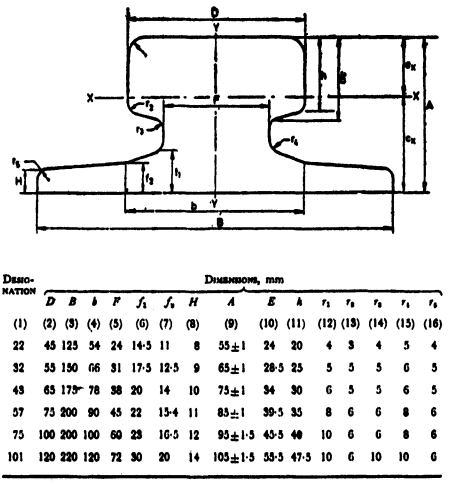
Rail is the main component of the railroad track. Its function is to guide the wheels of the rolling stock forward, to withstand the enormous pressure of the wheels and to transmit it to the rail sleepers. The rail must provide a continuous, smooth and minimum resistance rolling surface for the wheels. In the electrified railway or automatic blocking section, the rail can also be used as a track circuit.
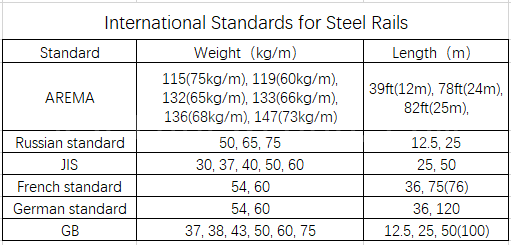 The specific standard content of the rail varies from country to country and region to region, the following are some examples of the main content of some countries and regions of the rail standard:
The specific standard content of the rail varies from country to country and region to region, the following are some examples of the main content of some countries and regions of the rail standard:
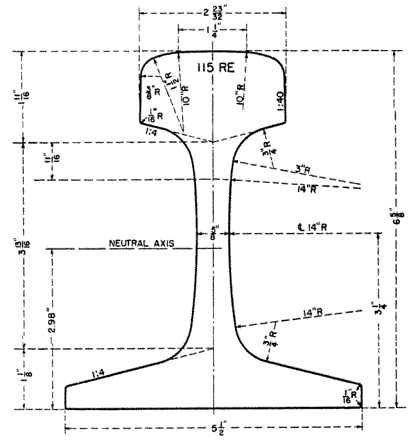
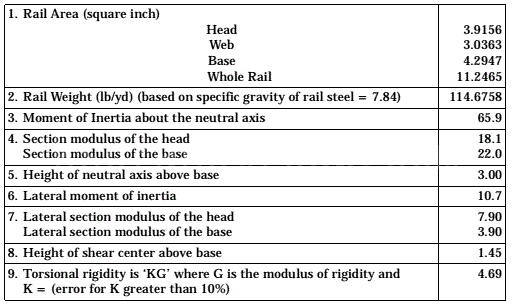
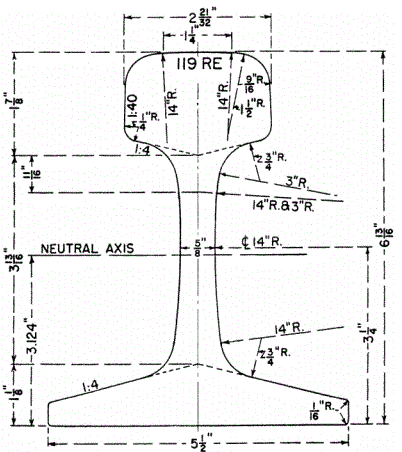
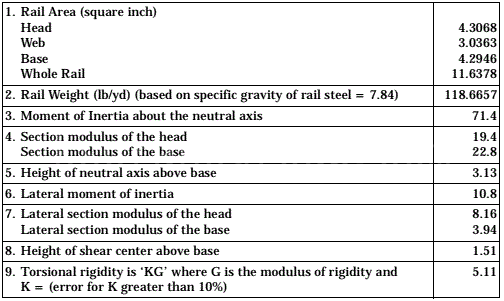

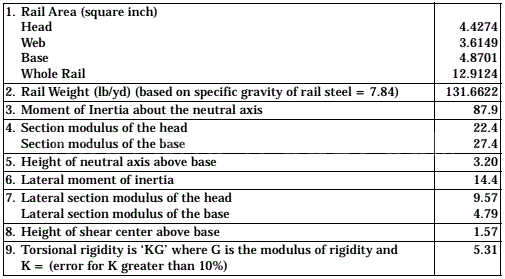
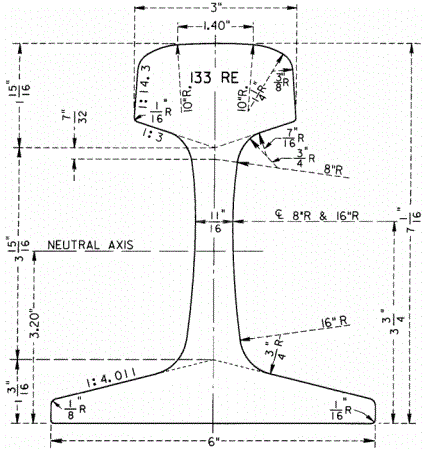
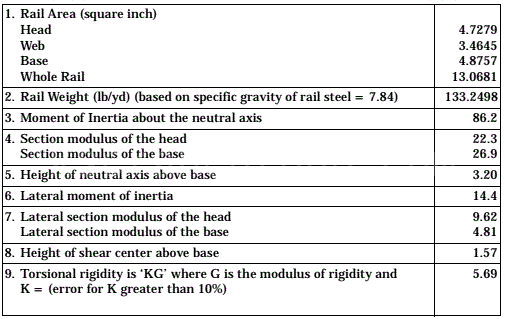
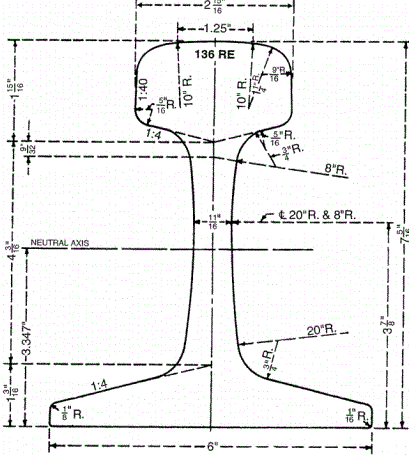
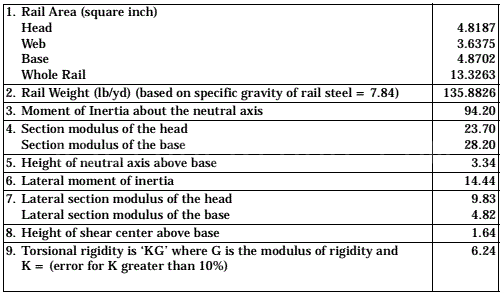
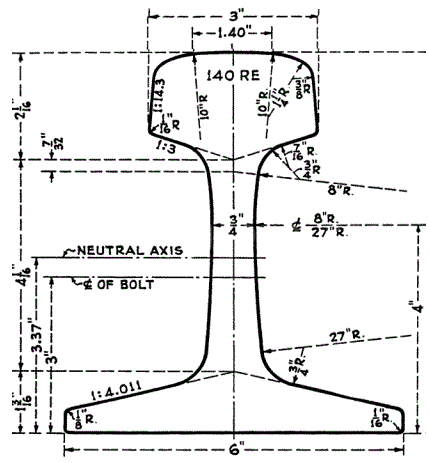
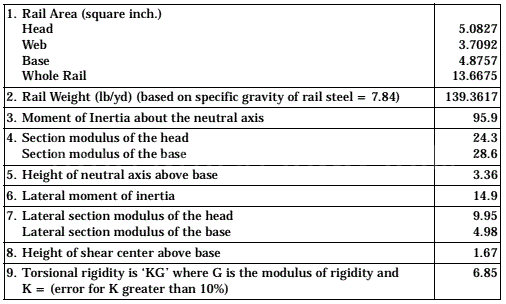
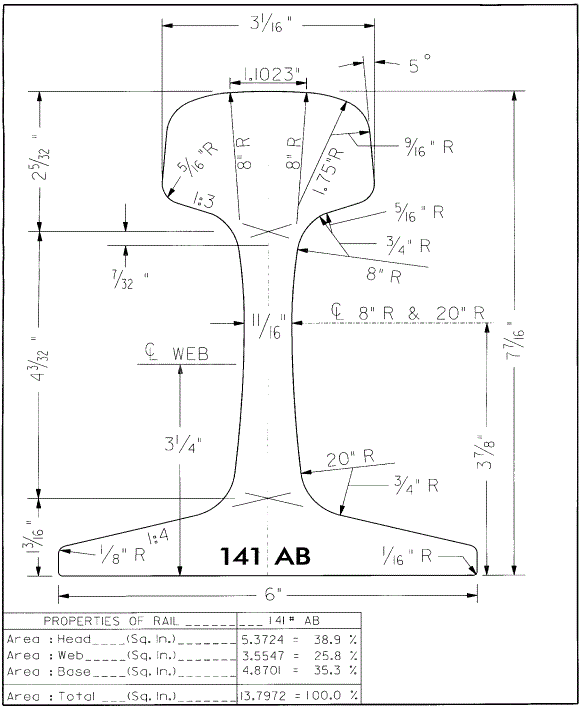
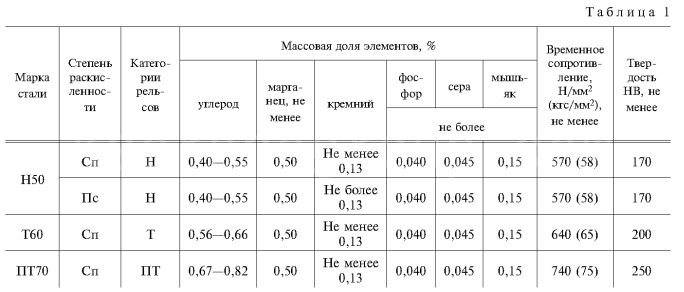
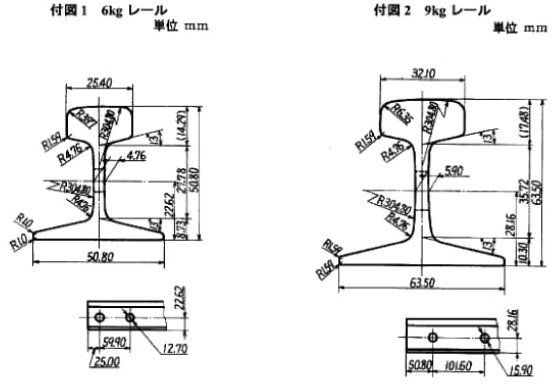
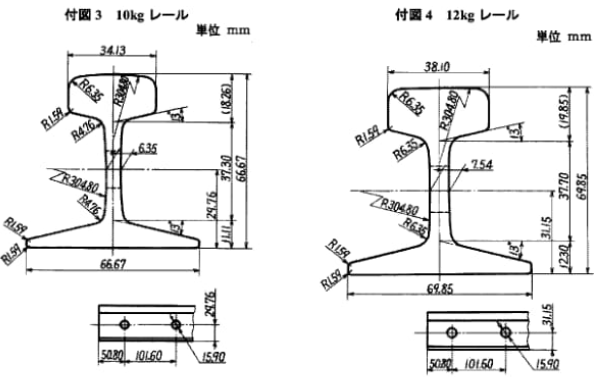
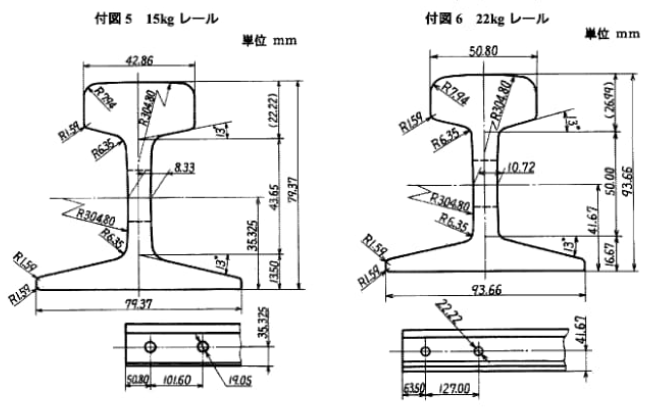
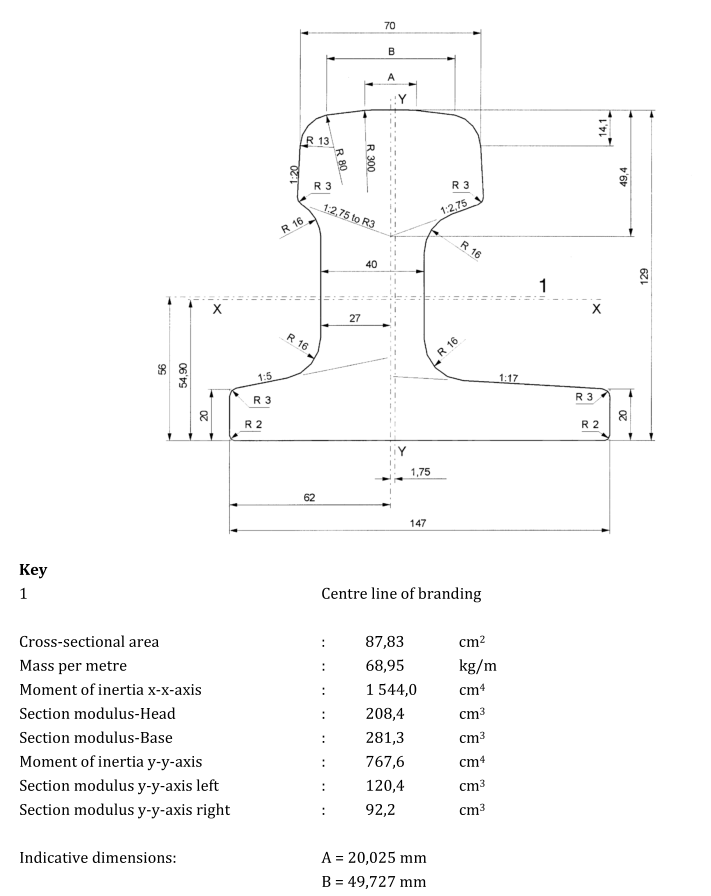
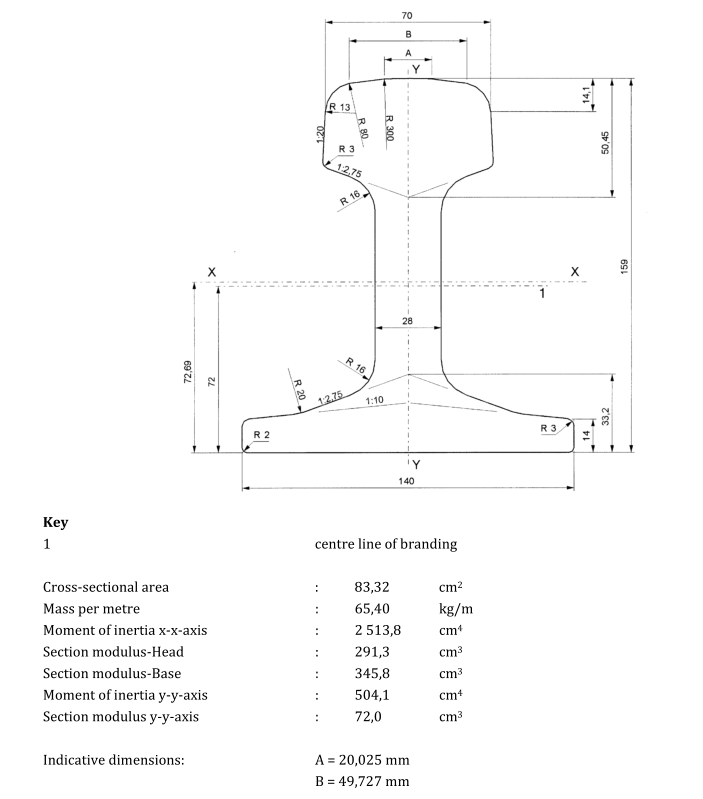
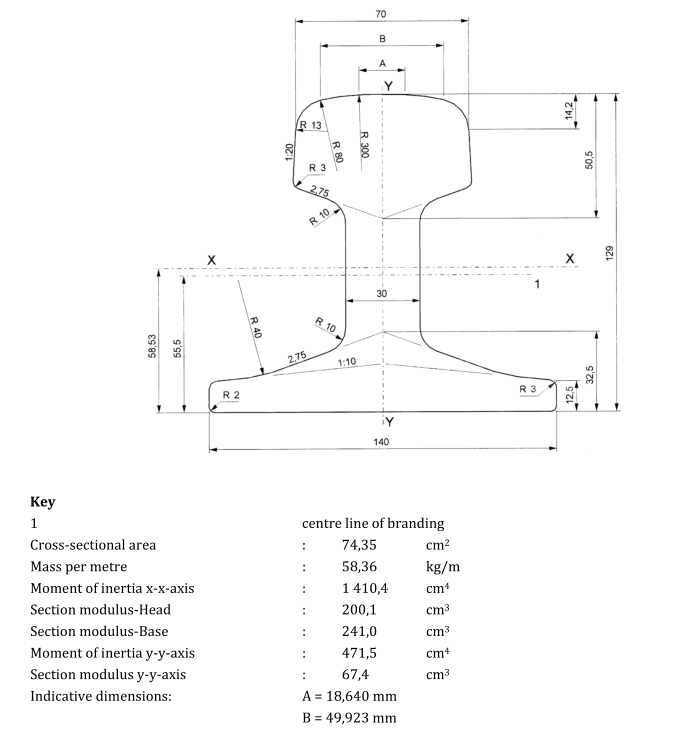
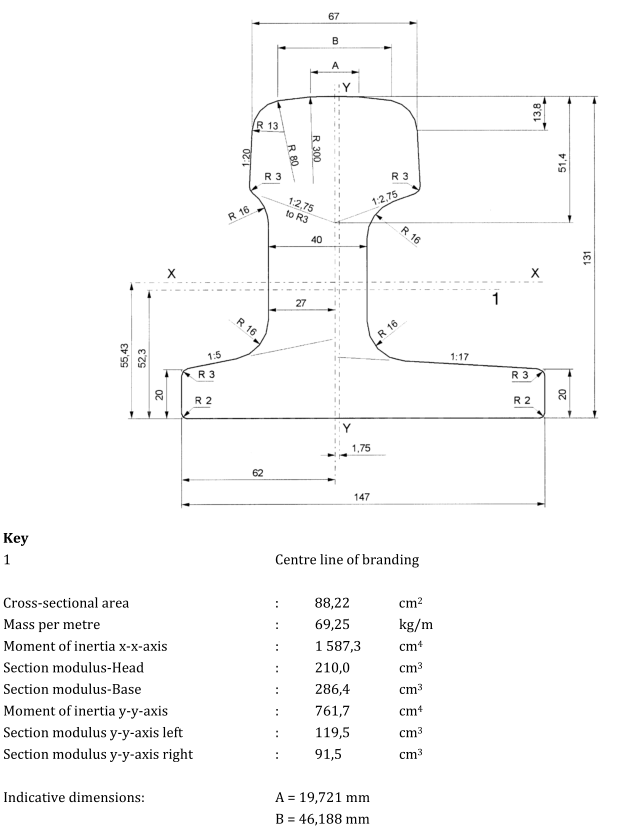
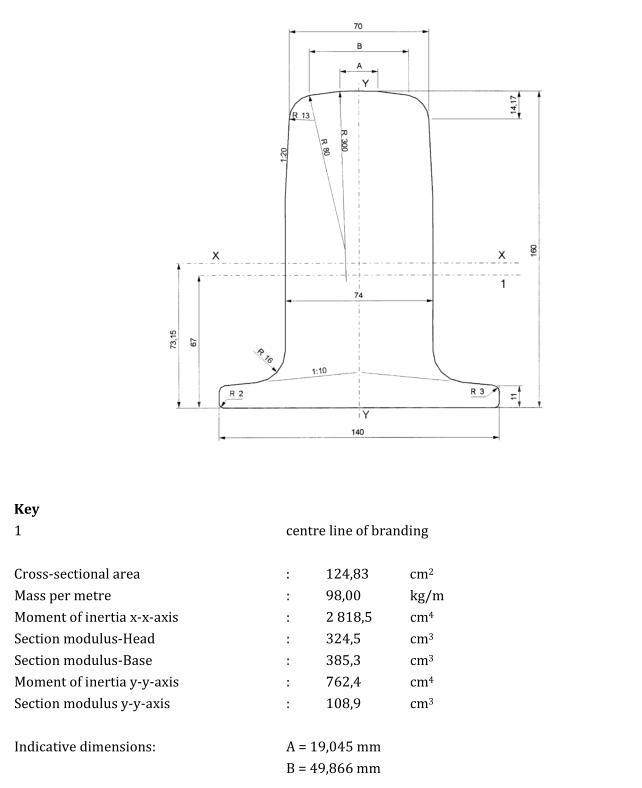
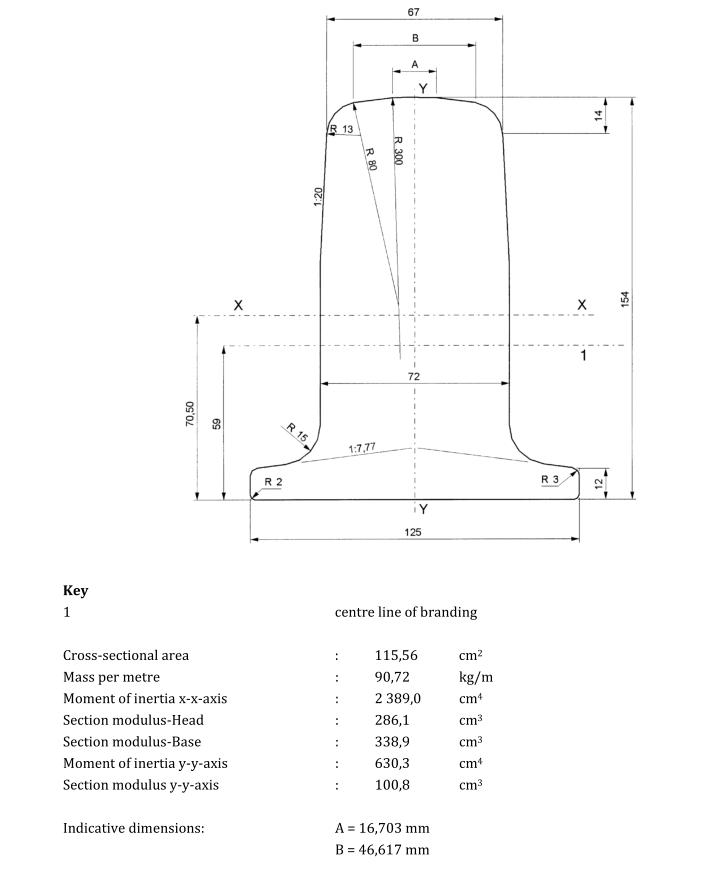
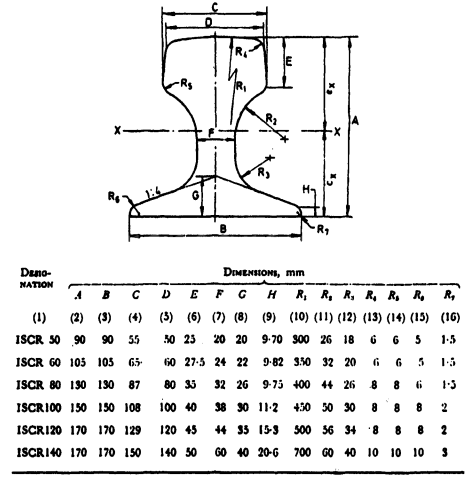
 Please note that the above are just some examples and different countries and regions may have more detailed regulations and requirements in their standards. To find out the specifics of a rail standard for a particular country or region, you can refer to the official documents of the relevant standards organization or contact your local railroad administration or railroad engineer for more detailed information. In addition, these standards are often updated and revised over time, so it is important to ensure that you consult the latest version of the standard for accurate information.
Please note that the above are just some examples and different countries and regions may have more detailed regulations and requirements in their standards. To find out the specifics of a rail standard for a particular country or region, you can refer to the official documents of the relevant standards organization or contact your local railroad administration or railroad engineer for more detailed information. In addition, these standards are often updated and revised over time, so it is important to ensure that you consult the latest version of the standard for accurate information.
 The specific standard content of the rail varies from country to country and region to region, the following are some examples of the main content of some countries and regions of the rail standard:
The specific standard content of the rail varies from country to country and region to region, the following are some examples of the main content of some countries and regions of the rail standard:
United States (AREMA standards)
The major railroads in the United States use a range of standards, including those developed by AREMA (American Railway Engineering and Maintenance of Way Association), such as AREMA 115, AREMA 132, and others. AREMA standards cover all types of rails, including tracks, crossovers, turnouts, and more. They include detailed specifications for rail geometry, material requirements, dimensions, welding requirements, heat treatment, coating and other performance parameters.












Russia (GOST standard)
The Russian railroad system uses standards developed by GOST (Russian State Standard), such as GOST 8161, GOST 5876, etc. The Russian railroad system is based on the GOST standards. GOST 8161 includes technical conditions for different types of steel for railroad tracks, including material, dimensions, mechanical properties, etc. GOST 5876 specifies the requirements for steel for railroad tracks. GOST 5876 specifies the size and shape requirements for rails.
China (GB/T standard)
Chinese rail standards are usually set by China Railway Corporation (CRCC) and the National Standardization Administration of China (NSAC), and some of the common standards include GB/T 3414, GB/T 6995, and GB/T 2585. GB/T 3414 specifies the technical conditions of common rail, including rail type, size, material composition, mechanical properties, etc. The standard is based on the standard of GB/T 6995 and GB/T 2585. GB/T 6995 specifies the technical conditions of rails for high-speed railroads, including material properties, dimensions and performance parameters of high-speed railroads. YB/T 5050 specifies the technical conditions of steel rails for cranes, including rail type, size, material composition, mechanical properties and so on.Japan (JIS standard)
Japanese rail standards are developed by the Japan Railway Standardization Society (JRSK) and the Japan Railway Technology Institute (RTRI), among others. Some of the Japanese standards for rails include JIS E 1101, JIS E 1103, etc. JIS E 1101 specifies the chemical composition, dimensions and mechanical property requirements of steel for rail. JIS E 1103 specifies the dimensional and geometric requirements for different types of rails.


Europe (EN and UIC standards)
The standards used in the European railroad system are mainly based on specifications developed by EN (European Standard) and UIC (International Union of Railways). Some common European rail standards include EN 13674, EN 13675, UIC 860 and others. The EN 13674 standard covers a wide range of different types of rails, including different rail types and track grades. It covers the material properties, dimensions, and mechanical requirements of rails, as well as heat treatment and welding requirements.





India (IS Standards)
Indian standards for steel rails are usually based on IS (Indian Standards Authority) such as IS 3443, IS 2062 etc. IS 3443 specifies the technical conditions of steel for rail, including chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensional and quality requirements of the material. IS 2062 specifies the technical conditions of steel for general railways.
 Please note that the above are just some examples and different countries and regions may have more detailed regulations and requirements in their standards. To find out the specifics of a rail standard for a particular country or region, you can refer to the official documents of the relevant standards organization or contact your local railroad administration or railroad engineer for more detailed information. In addition, these standards are often updated and revised over time, so it is important to ensure that you consult the latest version of the standard for accurate information.
Please note that the above are just some examples and different countries and regions may have more detailed regulations and requirements in their standards. To find out the specifics of a rail standard for a particular country or region, you can refer to the official documents of the relevant standards organization or contact your local railroad administration or railroad engineer for more detailed information. In addition, these standards are often updated and revised over time, so it is important to ensure that you consult the latest version of the standard for accurate information.
Do you like what we do?Share it

















































